Background
Canadian Forces Base (CFB) 5 Wing Goose Bay was founded by the Canadian and U.S. military forces and played an important and strategic role during World War II as a refueling base for aircraft en route to Europe. Goose Bay met several key criteria for such a base: it is on the main flying path to Europe; the area is generally fog-free; and it has a nearby harbour suitable for deep sea shipping. Between 1942 and 1945, over 24,000 Canadian and U.S. aircraft landed at Goose Bay on their way to Europe. U.S. military activity remained high in the 1950s and 1960s, and at peak, over 12,000 personnel were stationed at the Base. The U.S. terminated its strategic air command operations at Goose Bay in 1976 and ceased all operations in 1991.
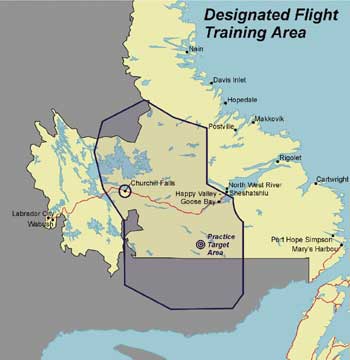
Today, CFB Goose Bay is world renowned as an area for low level flight training and interest is rising. Flight training at Goose Bay dates back to the 1950s when the Royal Air Force began low level flying at the Base. In 1981, the German Air Force began operations at Goose Bay. |
| |
| |
| |
 |
|
|
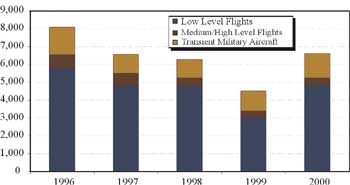
| Military Flights
1996-2000 |
 |
|
| |
| Source: Department of National Defence |
| |
Increasing interest in low level flying at Goose Bay led Canada to sign a
Multinational Memorandum of Understanding (MMOU) in 1986 with the United States, United Kingdom and Germany. This MMOU provided the authority for low level flying in the area by NATO partners, and committed participants to long-term arrangements at the Base. The Netherlands signed the MMOU in 1987.
The 1986 MMOU was renewed in 1996 for another 10 year period with the United Kingdom, Germany, and the Netherlands. The current memorandum allows for up to 15,000 low level and 3,000 medium/high level training flights annually. Italy signed the memorandum in 2000. France, Belgium and Norway have indicated they will conduct trial deployments at Goose Bay in 2001.
What is Low Level Flying?
Military flight training includes flying at low altitude to simulate certain defence procedures. Military analysts indicate that in recent international tensions (e.g., the Gulf War and Kosovo Crisis) low level flights were essential. To practice these skills, military aircraft fly at
altitude as low as 100 feet above terrain level and practice dropping non-explosive bombs at a controlled target range.
|
| |
| Low Level Flying
continued on next page. |
| |
| Map: Department of National Defence |
|

